There is a new normal in America: Our government may shut down, but our wars continue.
Congress may not be able to pass a budget, but the U.S. military can still launch commando raids in Libya and Somalia, the Afghan War can still be prosecuted, Italy can be garrisoned by American troops (putting the “empire” back in Rome), Africa can be used as an imperial playground (as in the late 19th century “scramble for Africa,” but with the United States and China doing the scrambling this time around), and the military-industrial complex can still dominate the world’s arms trade.
| Americans ought to think about war not just as an extreme exercise of politics, but also as a continuation of exploitative commerce by other means. Combat as commerce. |
In the halls of Congress and the Pentagon, it’s business as usual, if your definition of “business” is the power and profits you get from constantly preparing for and prosecuting wars around the world. “War is a racket,” General Smedley Butler famously declared in 1935, and even now it’s hard to disagree with a man who had two Congressional Medals of Honor to his credit and was intimately familiar with American imperialism.
Once upon a time, as a serving officer in the U.S. Air Force, I was taught that Carl von Clausewitz had defined war as a continuation of politics by other means. This definition is, in fact, a simplification of his classic and complex book, On War, written after his experiences fighting Napoleon in the early nineteenth century.
The idea of war as a continuation of politics is both moderately interesting and dangerously misleading: interesting because it connects war to political processes and suggests that they should be fought for political goals; misleading because it suggests that war is essentially rational and so controllable. The fault here is not Clausewitz’s, but the American military’s for misreading and oversimplifying him.
Perhaps another “Carl” might lend a hand when it comes to helping Americans understand what war is really all about. I’m referring to Karl Marx, who admired Clausewitz, notably for his idea that combat is to war what a cash payment is to commerce. However seldom combat (or such payments) may happen, they are the culmination and so the ultimate arbiters of the process.
War, in other words, is settled by killing, a bloody transaction that echoes the exploitative exchanges of capitalism. Marx found this idea to be both suggestive and pregnant with meaning. So should we all.
Following Marx, Americans ought to think about war not just as an extreme exercise of politics, but also as a continuation of exploitative commerce by other means. Combat as commerce: there’s more in that than simple alliteration.
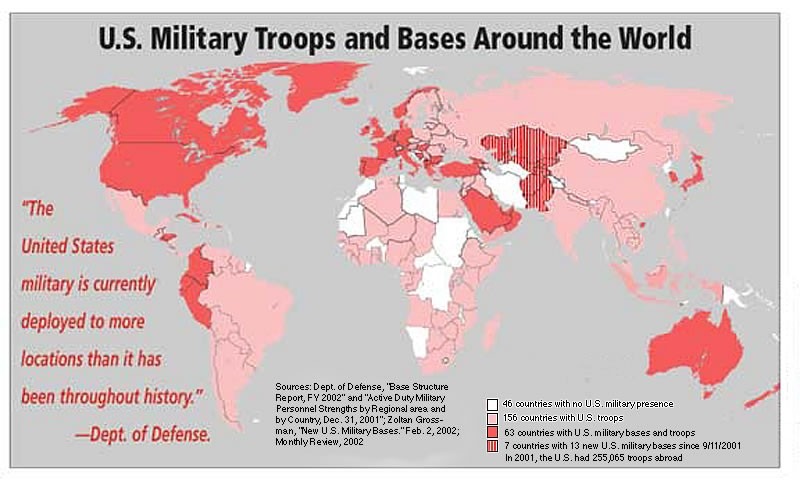
In the history of war, such commercial transactions took many forms, whether as territory conquered, spoils carted away, raw materials appropriated, or market share gained. Consider American wars. The War of 1812 is sometimes portrayed as a minor dust-up with Britain, involving the temporary occupation and burning of our capital, but it really was about crushing Indians on the frontier and grabbing their land. The Mexican-American War was another land grab, this time for the benefit of slaveholders. The Spanish-American War was a land grab for those seeking an American empire overseas, while World War I was for making the world “safe for democracy”—and for American business interests globally.
Even World War II, a war necessary to stop Hitler and Imperial Japan, witnessed the emergence of the United States as the arsenal of democracy, the world’s dominant power, and the new imperial stand-in for a bankrupt British Empire.
Korea? Vietnam? Lots of profit for the military-industrial complex and plenty of power for the Pentagon establishment. Iraq, the Middle East, current adventures in Africa? Oil, markets, natural resources, global dominance.
In societal calamities like war, there will always be winners and losers. But the clearest winners are often companies like Boeing and Dow Chemical, which provided B-52 bombers and Agent Orange, respectively, to the U.S. military in Vietnam. Such “arms merchants”—an older, more honest term than today’s “defense contractor”—don’t have to pursue the hard sell, not when war and preparations for it have become so permanently, inseparably intertwined with the American economy, foreign policy, and our nation’s identity as a rugged land of “warriors” and “heroes” (more on that in a moment).
Consider one more definition of war: not as politics or even as commerce, but as societal catastrophe. Thinking this way, we can apply Naomi Klein’s concepts of the “shock doctrine” and “disaster capitalism” to it. When such disasters occur, there are always those who seek to turn a profit.
Most Americans are, however, discouraged from thinking about war this way thanks to the power of what we call “patriotism” or, at an extreme, “superpatriotism” when it applies to us, and the significantly more negative “nationalism” or “ultra-nationalism” when it appears in other countries. During wars, we’re told to “support our troops,” to wave the flag, to put country first, to respect the patriotic ideal of selfless service and redemptive sacrifice (even if all but 1 percent of us are never expected to serve or sacrifice).
We’re discouraged from reflecting on the uncomfortable fact that, as “our” troops sacrifice and suffer, others in society are profiting big time. Such thoughts are considered unseemly and unpatriotic. Pay no attention to the war profiteers, who pass as perfectly respectable companies. After all, any price is worth paying (or profits worth offering up) to contain the enemy—not so long ago, the red menace, but in the twenty-first century, the murderous terrorist.
Forever war is forever profitable. Think of the Lockheed Martins of the world. In their commerce with the Pentagon, as well as the militaries of other nations, they ultimately seek cash payment for their weapons and a world in which such weaponry will be eternally needed. In the pursuit of security or victory, political leaders willingly pay their price.
Call it a Clausewitzian/Marxian feedback loop or the dialectic of Carl and Karl. It also represents the eternal marriage of combat and commerce. If it doesn’t catch all of what war is about, it should at least remind us of the degree to which war as disaster capitalism is driven by profit and power.
For a synthesis, we need only turn from Carl or Karl to Cal—President Calvin Coolidge, that is. “The business of America is business,” he declared in the Roaring Twenties. Almost a century later, the business of America is war, even if today’s presidents are too polite to mention that the business is booming.
Many young people today are, in fact, looking for a release from consumerism. In seeking new identities, quite a few turn to the military. And it provides. Recruits are hailed as warriors and warfighters, as heroes, and not just within the military either, but by society at large.
Yet in joining the military and being celebrated for that act, our troops paradoxically become yet another commodity, another consumable of the state. Indeed, they become consumed by war and its violence. Their compensation? To be packaged and marketed as the heroes of our militarized moment. Steven Gardiner, a cultural anthropologist and U.S. Army veteran, has written eloquently about what he calls the “heroic masochism” of militarized settings and their allure for America’s youth. Put succinctly, in seeking to escape a consumerism that has lost its meaning and find a release from dead-end jobs, many volunteers are transformed into celebrants of violence, seekers and givers of pain, a harsh reality Americans ignore as long as that violence is acted out overseas against our enemies and local populations.
Such “heroic” identities, tied so closely to violence in war, often prove poorly suited to peacetime settings. Frustration and demoralization devolve into domestic violence and suicide. In an American society with ever fewer meaningful peacetime jobs, exhibiting greater and greater polarization of wealth and opportunity, the decisions of some veterans to turn to or return to mind-numbing drugs of various sorts and soul-stirring violence is tragically predictable. That it stems from their exploitative commodification as so many heroic inflictors of violence in our name is a reality most Americans are content to forget.
As Russian revolutionary Leon Trotsky pithily observed, “You may not be interested in war, but war is interested in you.” If war is combat and commerce, calamity and commodity, it cannot be left to our political leaders alone—and certainly not to our generals. When it comes to war, however far from it we may seem to be, we’re all in our own ways customers and consumers. Some pay a high price. Many pay a little. A few gain a lot. Keep an eye on those few and you’ll end up with a keener appreciation of what war is actually all about.
No wonder our leaders tell us not to worry our little heads about our wars—just support those troops, go shopping, and keep waving that flag. If patriotism is famously the last refuge of the scoundrel, it’s also the first recourse of those seeking to mobilize customers for the latest bloodletting exercise in combat as commerce.
Just remember: In the grand bargain that is war, it’s their product and their profit. And that’s no bargain for America, or for that matter for the world.
William Astore is a regular writer at TomDispatch.com (where this article first appeared). He is a retired lieutenant colonel (USAF).






0 Comments